The ancient Celtiberians
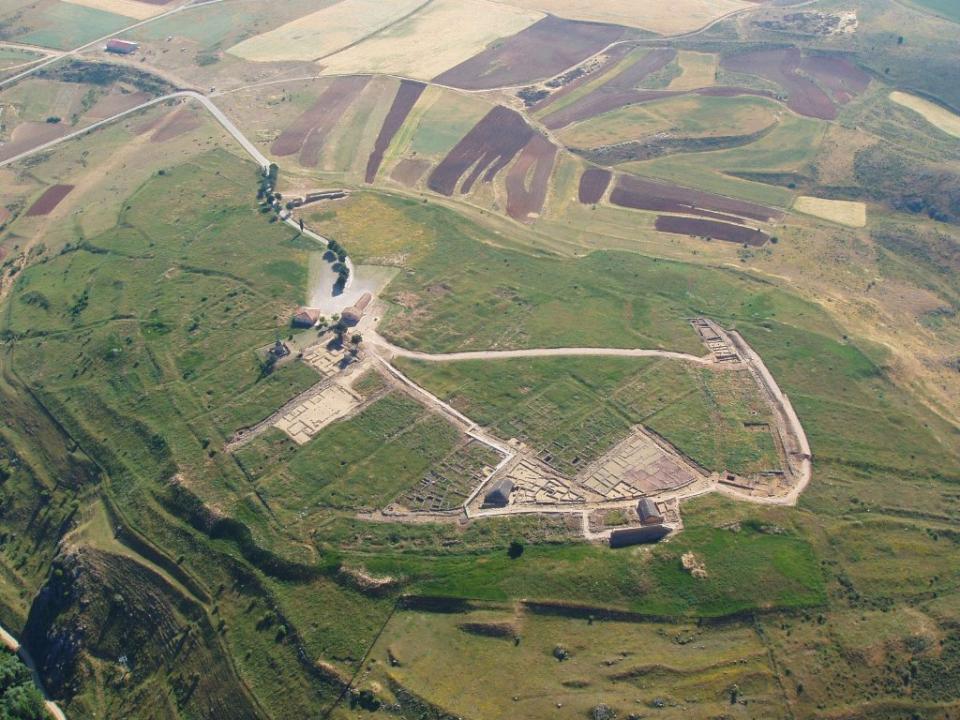
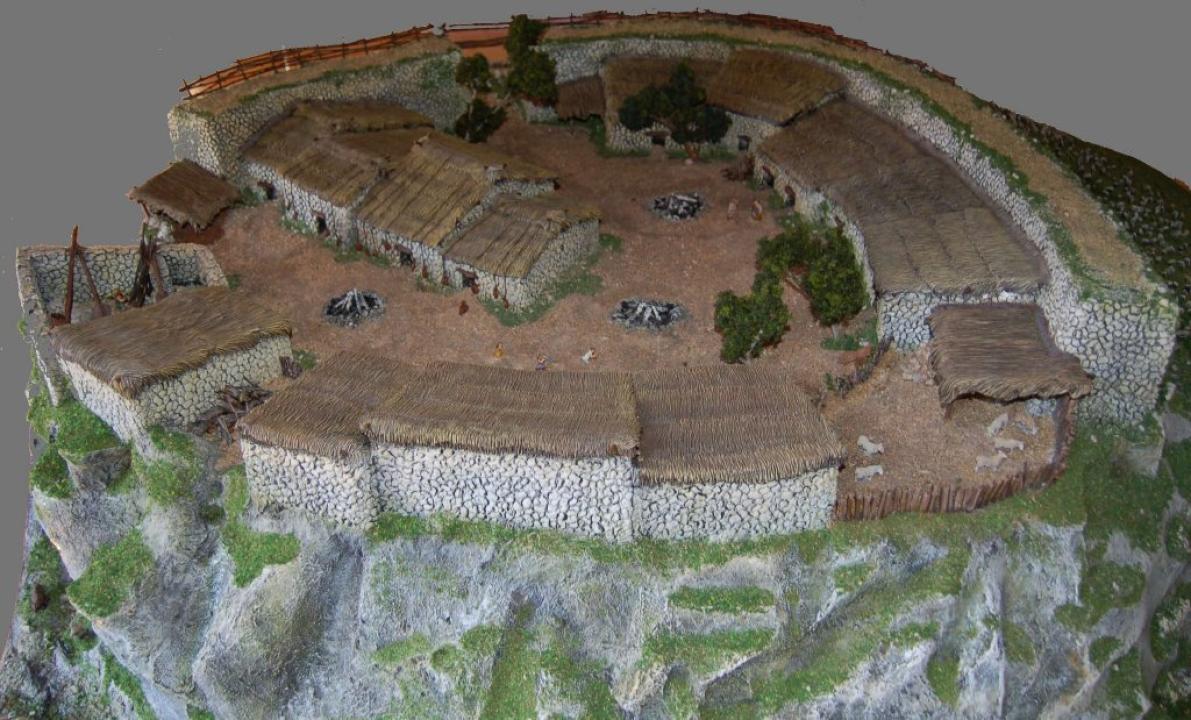
By the seventh century BCE advanced elements or languages of the mountain ridges of the Iberian and Central will be dotted with small settlements, about one hectare. Giving priority to choose locations castellated elements and visibility issues that are exacerbated by the construction of powerful defensive systems, consisting of wide walls with defensive towers to control access, moats and stone strips bowing to destabilize the attackers.
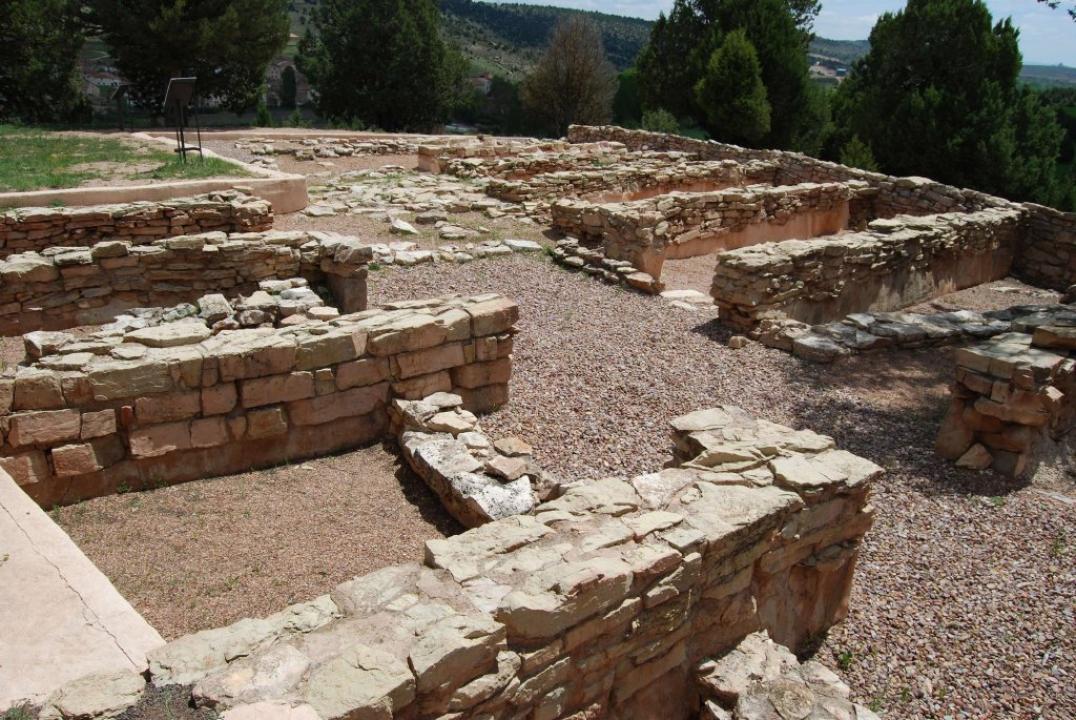
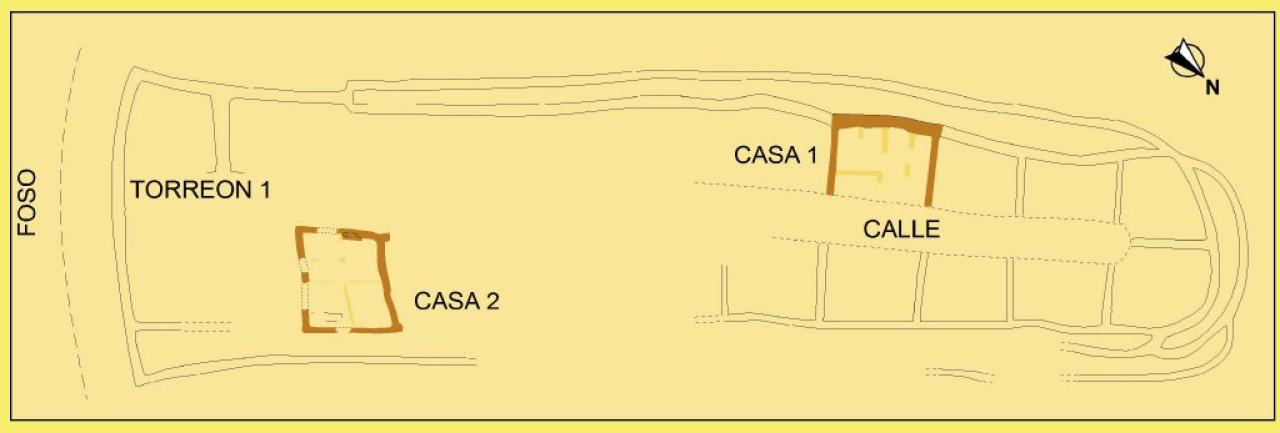
At the same time prominent hills in the valleys of the Alto Tajo Alto Jalon and shows the settlement of small villages of rectangular houses arranged around a central space or street, bordered by stone walls, as seen in the town of Ceremeño (Herraria , Guadalajara), the loft.
- Rural Settlements
During the fourth century BCE a number of forts were deserted along accusing the fourth and third centuries BC, a number of important changes in the landscape, resulted in an increase of villages, some larger, and burial, reflecting a population increase, showing preference to occupy prominent hills in the wide plains suitable for rainfed agriculture.
During the third century BCE is consolidated in the Upper Douro, agricultural economic orientation, embodied in rural settlements of mixed economy, with an increase in the intensification of trade and commerce. This was articulated with the internal evolution of its institutions, will crystallize before the Roman conquest in the creation of cities, which enable the development of handicraft and services that make the difference between country and city.
-Cities
The Romans found a structured and hierarchical landscape of cities and their territories. Cities appear as organizing centers, political and administrative territories and incorporate writing, using the Iberian signario to translate their Celtic language, and coinage, and Roman under concession
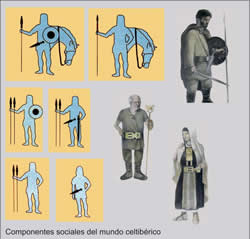
Cities are those that deal directly with Rome, being received and whether that sign agreements indicating that they are true city-states. In this context the feeling of belonging to communities or large populi (Arevacos, pelendones, Titos and belos) where the social structure was based on kinship relations will be mediated by new forms of personal dependence imposed by urban structure. The city will now be the primary referent of identity.