The Roman conquest brought a series of transformations in the world Celtiberian, manifested in a gradual acculturation, known as romanization, which affected all aspects of Indian life.
It involved the introduction of Roman urban organization and culture, adapted to the reality celtiberica: construction of new buildings, coinage, use of writing, gradual adoption of Latin, use of objects and clothes Roman assimilation of cults and gods. However, the romanization was not the same as for a long time they continued living together with other indigenous Romanized environments.
The city as an instrument of Romanization
In a century of almost Modified radical Celtiberia, using the city as an instrument of Romanization and territorial control center, applying this policy in two phases: one from the late second century BC and one from mid-first century BCE and another with the change and was starting
- First territorial restructuring: the cities on the flat (for s.II BC)
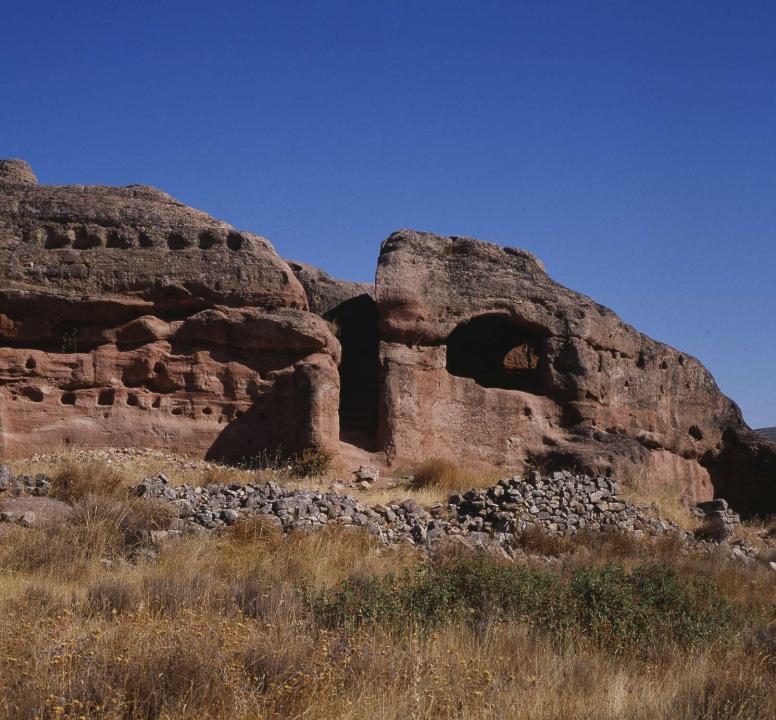
The Roman impact on settlements began to accuse and after the Wars Cel (after 133 BC) with the installation of a number of towns in new plant in areas with agricultural or mineral resources, which have been called " in plain. " Would be populated by indigenous Romanized, italics immigrants and war veterans settled.
Aragon
- Segeda II, Duron de Belmonte (Z)
- Valdeherrera, Calatayud (Z)
- La Caridad, Caminreal (TE)
- Alto Chacon, Teruel
- Herrera de los Navarros (Z)
- El Castellar, El Berrueco (Z)
- Ojos Negros-yac metalurgicos (TE)
Castilla y Leon
- Uxama, Osma (SO)
- Tiermes, Montejo de Tiermes (SO)
- Second territorial restructuring (second half century BC):
From mid-first century BCE profound changes occurred with the transfer of cities and its people, keeping them the name of the previous indigenous core, only in the Alto Douro is maintained at the same site. The initial time must be dated in time of Caesar, but to the rise will take place with Augustus.
From Octavio many cities municipal reached the range, which led the monumentalization of its buildings and the dissemination and standardization of many aspects of material culture. Thus, architecture, sculptures and accompanied by captions, was a highly effective means to transmit the ideology of power.
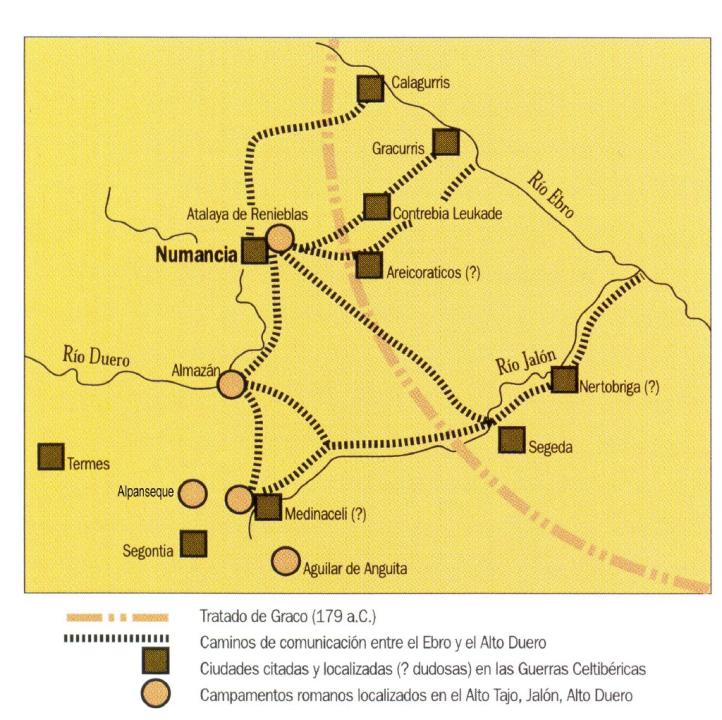
He also received major boost trade in goods and movement of people, brought about by two main Roman roads crossing the area, one that linked Caesaraugusta (Zaragoza) with Asturica (Astorga) and Emerita Augusta (Merida) and another that linked Nertobrigas (Calatorao ? and Bilbilis (Calatayud) with Segontia.
However, the tombstones show the survival of indigenous and other groups suprafamiliares stelae, decorated with the figure of the rider, reflect the effect of a full of connotations iconographic type known in Clunia, Lara de los Infantes (Burgos), Segovia, Borobia (Soria).
Urban centers are now set on newly created settlements or small settlements previous Celtiberian:
Aragon
- Bilbilis Italica, Calatayud (Z)
- Arcobriga, Monreal de Ariza (Z)
- San Esteban, El Poyo del Cid (TE)
Castilla y Leon
- Augustobriga, Muro (SO) Numancia, Garray (SO)
- Uxama, Osma (SO)
- Tiermes, Montejo de Tiermes (SO)
- Clunia, Peñalba de Castro (BU)
Castilla-La Mancha
- Segobriga
- Ercavica - Contrebia Carbica
Rioja
- Contrebia Leukade, Inestrillas